Work is underway at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (SEA) to be the first airport in the nation to use a special cleaning technology that more fully removes foam containing PFAS (per- […]
Work is underway at Seattle-Tacoma International Airport (SEA) to be the first airport in the nation to use a special cleaning technology that more fully removes foam containing PFAS (per- […]
Amberjack Capital Partners, a private equity investment firm focused on building market leaders across the industrial, infrastructure and environmental sectors, announced the successful exit of its investment in Best Trash, […]
University of Delaware and Argonne National Laboratory have come up with a chemical reaction that can convert Styrofoam into a high-value conducting polymer known as PEDOT:PSS. In a new paper […]
The Montgomery County Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) is now offering plastic film recycling services at the Shady Grove Transfer Station and Recycling Center in Derwood. Plastic film are flexible […]
The U.S. Department of Labor is seeking nominations for four representative positions on the National Advisory Committee on Occupational Safety and Health for terms scheduled to expire in 2025. The […]
Element Six (E6), a pioneer in the development and manufacturing of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) diamond solutions, and Lummus Technology, a global provider of process technologies and value-driven energy solutions, […]
Montrose Environmental Group, Inc., a high-growth global environmental solutions company, and Waste Connections, shared insight into the use of Montrose’s patented per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) treatment system to address […]
Google supports app providing recycling info globally With the help of a Google program, Swedish recycling app Bower is expanding its AI-visioning model worldwide, aiming for a world without waste. Continue Reading→ The post Google supports app providing recycling info globally appeared first on Resource Recycling News.
WM upgrade in Wisconsin leverages location, community With a $39 million upgrade completed at one of its biggest MRFs, WM officials are looking to further refine automation capabilities as well as add volumes in the Midwest. Continue Reading→ The post WM upgrade in Wisconsin leverages location, community appeared first on…
Changing material stream drives Eureka MRF upgrades Minneapolis nonprofit MRF operator Eureka Recycling is seeing larger volumes of smaller plastics coming through its doors, creating challenges to maintain the same level of material quality. These changes spurred the company to plan substantial facility upgrades, a co-president said this week. Continue…
Novolex used less recycled plastic last year Putting AI and robotics into a MRF is one thing. Designing a MRF with AI and robotics makes for an entirely different experience, according to AMP founder and CEO Matanya Horowitz. Continue Reading→ The post Novolex used less recycled plastic last year appeared…
Recycling plastics is an essential practice in the fight against environmental pollution and resource depletion. However, the variety of plastics used in everyday products can make recycling a complex task. Not all plastics are created equal, and recognizing the different types of recyclable plastics is crucial for effective recycling. In this guide, we will explore the main types of recyclable plastics, their identifying symbols, and the significance of sorting them correctly to ensure they are processed efficiently.
By properly identifying and sorting plastics, we can significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and oceans. Each type of plastic has unique properties and recycling processes, making it important to understand these distinctions. This knowledge empowers individuals and organizations to contribute to a more sustainable future, where recycled materials are reused to create new products, conserving resources and minimizing environmental impact.
Symbol:
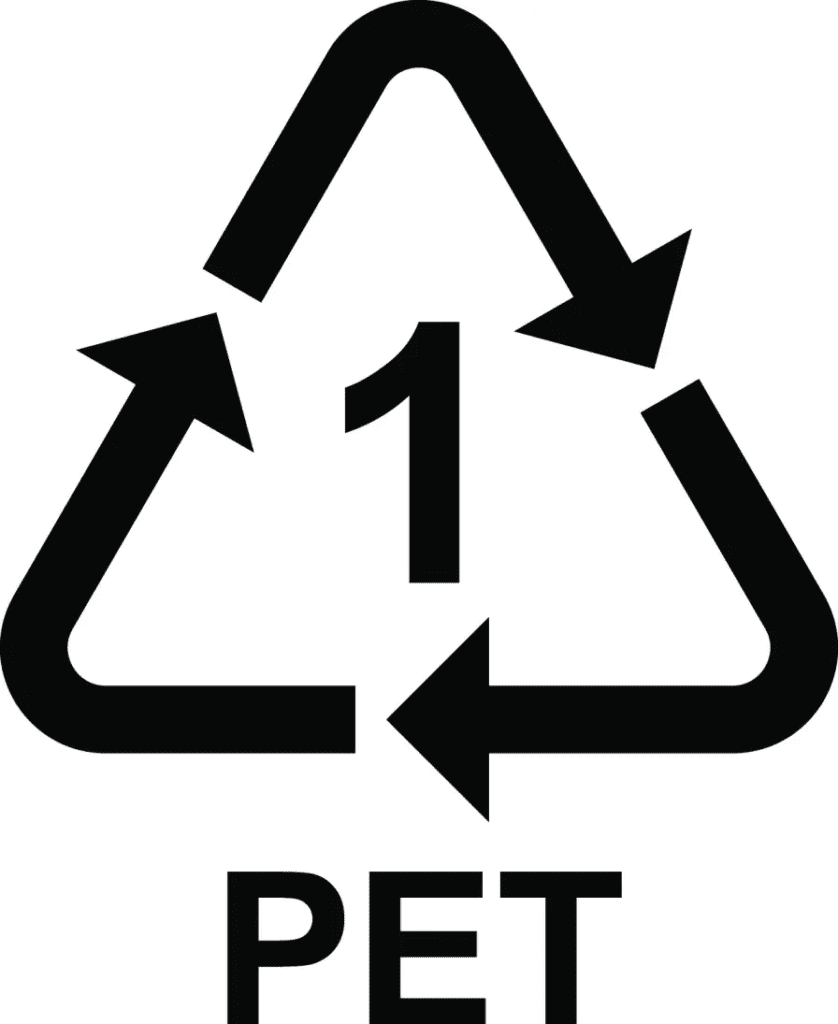

Description: PET is commonly used in beverage bottles, food containers, and packaging. It is clear, strong, and lightweight.
Identification: Look for the number “1” inside the recycling symbol. PET is often used for single-use plastic bottles and is widely accepted by recycling programs.
Importance of Sorting: Properly sorting PET helps in creating new products like clothing, carpets, and new containers.
Symbol:


Description: HDPE is a durable plastic used in milk jugs, detergent bottles, and some plastic bags. It is resistant to chemicals and moisture.
Identification: The number “2” inside the recycling symbol identifies HDPE. It can be translucent or opaque.
Importance of Sorting: HDPE can be recycled into new bottles, pipes, and plastic lumber. Proper sorting ensures that it can be processed efficiently.
Symbol:


Description: PVC is used in plumbing pipes, vinyl flooring, and some food packaging. It is known for its rigidity and chemical resistance.
Identification: The number “3” inside the recycling symbol denotes PVC. It can be clear or colored.
Importance of Sorting: PVC recycling is less common due to the release of harmful chemicals during processing. Proper sorting is crucial to avoid contamination.
Symbol:


Description: LDPE is used in plastic bags, shrink wrap, and flexible bottle tops. It is less rigid than HDPE and has a lower melting point.
Identification: The number “4” inside the recycling symbol indicates LDPE. It is often found in thin, flexible forms.
Importance of Sorting: LDPE can be recycled into bin liners, floor tiles, and shipping envelopes. Proper sorting helps in reducing plastic bag waste.
Symbol:


Description: PP is commonly found in yogurt containers, bottle caps, and straws. It is tough and resistant to heat.
Identification: The number “5” inside the recycling symbol represents PP. It can be opaque or colored.
Importance of Sorting: PP can be recycled into signal lights, battery cables, and automotive parts. Correct sorting enhances the quality of recycled products.
Symbol:


Description: PS is used in disposable coffee cups, plastic food boxes, and packing peanuts. It can be rigid or foam.
Identification: The number “6” inside the recycling symbol denotes PS. It is often seen in both solid and foam forms.
Importance of Sorting: PS recycling is challenging due to its bulkiness and low density. Proper sorting is essential to prevent contamination and facilitate recycling into insulation and other products.
Symbol:


Description: This category includes various plastics like acrylic, nylon, and polycarbonate. These are used in a wide range of products, from sunglasses to computer cases.
Identification: The number “7” inside the recycling symbol indicates miscellaneous plastics. They vary widely in properties and uses.
Importance of Sorting: Recycling for this category depends on the specific type of plastic. Proper sorting ensures that recyclable materials are not mixed with non-recyclable ones.
Properly sorting recyclable plastics is essential for several reasons:
By understanding the different types of recyclable plastics and how to identify them, we can all contribute to a more efficient and effective recycling system. At IMPACT Recycling Partners, we are committed to promoting proper recycling practices and ensuring that plastics are sorted correctly to maximize their reuse and reduce environmental impact. Let’s work together to make a difference!